
#Law of diminishing returns how to
Yet again, these two related yet distinct ideas can help you further your understanding of this law and how to apply it in your specific business situation.ĭiminishing productivity occurs, similar to diminishing returns, when one input is changed while the others are fixed.
Related: How Businesses Can Leverage Tech for Optimal Business Insurance What is the difference between diminishing vs.

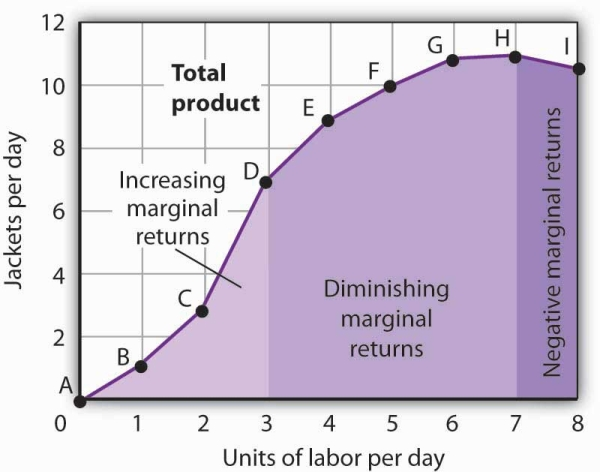
Too many workers can cause crowding, too much pesticide can kill crops and too much energy can cause an explosion. This marginal productivity refers explicitly to decreasing the additional output or productivity that occurs when applying an input while holding all others constant.Īt this point, the input increases too much and is, in effect, nullified: The input is oversaturated, and the output no longer increases. If the output exceeds the input increase, it is "increasing returns to scale." And if the output is less than the input increase, you have "decreasing returns to scale." If the increase in output is proportional to the increase in inputs, then the business identifies this relationship as "constant returns to scale." Returns to scale describe the relationship between a proportional increase of all inputs, thus increasing or decreasing the output. This only occurs because that one singular input is affected, eventually decreasing it. The marginal output from that input will always eventually start to decline. These two concepts are often thrown around and misunderstood but are crucial to understanding the concept of marginal returns.ĭiminishing marginal returns happen when a business increases one singular input while maintaining all other inputs.
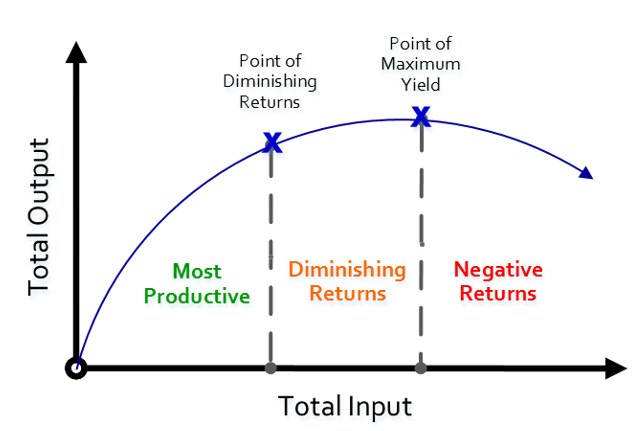
What's the difference between diminishing marginal returns and returns to scale? Since the wage you pay remains the same, you are increasing your cost of production in a manner inconsistent with your rate of product increases.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
